Software testing is a critical process in the SDLC, short for Software Development Lifecycle. It is a comprehensive process comprising specific methods and tools that aid in verifying and validating
Software testing is a critical process in the SDLC, short for Software Development Lifecycle. It is a comprehensive process comprising specific methods and tools that aid in verifying and validating that software applications do not have any bugs. The process also makes sure that software meets the standards set by the Design and Development team and efficiently and effectively satisfies user requirements.
What Is Software Testing?
Software Testing is a structured and systematic process of assessing that a software application works correctly and meets the pre-defined technical specifications. It checks the functionality, security, and efficiency of the software application, including compliance with modern assessment standards such as CodeSignal proctoring. The primary objective of software testing is to determine whether the software contains any bugs. Most development teams aim to detect bugs as early as possible in the software development lifecycle. It is a key process that improves overall quality of the product, boost user experience, and minimizes development costs.
Essentially, the software testing can be divided into two main steps:
- Verification: Mainly, in this step, we check whether the software is functioning in a way it is supposed to.
- Validation: In this step, we assess whether the software aligns with the customer’s needs and requirements. This step answers your question “Am I building the right product for my customers?”
What Is the Need for Software Testing?

Though testing can prove to be costly, organizations can save millions of dollars annually in development and support by executing efficient testing techniques and QA processes. Early software testing is extremely critical as it recognizes issues before the product is introduced in the market. If the development teams get the feedback on their product early in the product development lifecycle, they can address those issues and prevent bugs from causing major problems later on. Broadly, software testing can detect the below-mentioned issues:
- Poor Design Decisions
- Architectural Flaws
- Incorrect or Invalid Functionality
- Scalability Issues
- Security Vulnerabilities
A Real-life Example That Explains the Importance of Software Testing
Consider the real-life example of the Delta Air Lines incident that occurred back in July 2024. A cybersecurity firm in the United States “CrowdStrike” released a software update that had a few flaws. This ultimately led to widespread system crashes across Microsoft Windows platforms. Among the airlines that experienced the most severe impact on operations was Delta Air Lines. Ultimately, thousands of flights had to be cancelled, and the losses were estimated to be around $500 million. This event explains the key importance of comprehensive testing, especially when you are incorporating third-party platforms into systems that are mission critical.
What Are the Advantages of Software Testing?

There are tremendous advantages that software testing offers that greatly improve your software development lifecycle and the final product:
1. Cost Savings:
Detailed software testing and effective quality assurance are important for cost management. Relying on proactive evaluations helps you mitigate the expenses that come with post-release bug detection and fixing. Early detection also prevents simple defects from growing into major and complex problems.
2. Enhanced Product Quality and Reliability:
Complete frameworks for software testing improve product quality and reliability. These two factors are quite critical in user satisfaction and market success. Robust methodologies for testing recognize and fix defects early on, reducing the risk of complex issues in the final product.
3. Improved Security:
In the present digital landscape, cybersecurity has emerged as a main concern. Testing focused on security aspects plays a key role in recognizing defects, ascertaining compliance with industry standards, and safeguarding user data. Modern testing methodologies help developers fortify the software’s defenses against advanced threats.
4. Quicker Development:
Software testing expedites development cycles by optimizing workflows and recognizing issues early on. By integrating agile methodologies early on, automation platforms enable teams to streamline speed and resource allocation. It emphasizes the main functionalities while also continuously validating quality.
5. Smooth Feature Integration:
The capability to incorporate new features in a smooth and disruption-free manner is a major benefit of complete testing. Effective testing fosters confidence among the developers, enabling developers to expand functionalities without sacrificing stability of functions. Modern testing frameworks facilitate smooth feature integration by recognizing possible areas of conflict within the code, greatly minimizing regression risks.
Difference Between Automated Testing and Manual Testing
When you implement software testing, you can implement it in two ways:
- Automated Testing
- Manual Testing
1. Manual Testing:
Manual testing can be defined as the process where testers manually implement test cases without the help of automation tools. Testers execute various actions such as clicking buttons, verifying outputs and entering text, simulating how an end-user can interact with the software. Manual testing is generally utilized for usability testing, exploratory testing, and when the application is so small that automated testing becomes unnecessary.
2. Automated Testing:
Automated testing leverages scripts and tools to automatically implement tests on software. This basic approach is advantageous for routine testing tasks and for larger platforms where you would have to implement the same tests multiple times. Automated testing makes sure that the software can be more quickly and consistently tested. It also minimizes human errors and enhances testing efficiency over time.
What Are the Different Levels in Software Testing?
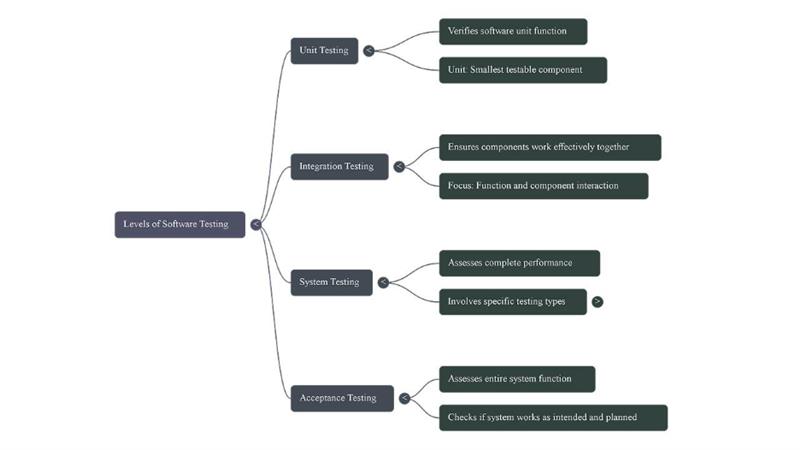
Essentially, software testing happens at 4 distinct levels or stages within the SDLC. Here, each emphasizes on specific parts of the application:
- Unit Testing
- Integration Testing
- System Testing
- Acceptance Testing
- Unit Testing: It verifies that every software unit functions as per the expectations. A unit can be defined as the smallest component of the application that can be tested.
- Integration Testing: Integration testing makes sure that software functions or components work effectively together.
- System Testing: System testing assesses complete performance of the system. This phase involves non-functional testing, functional testing, interface testing, recovery testing, and stress testing.
- Acceptance Testing: It assesses whether the entire system functions as intended and planned.
What Are the Different Types of Software Testing?
At all levels mentioned in the previous section, software testing differs in various types. Broadly, they can be classified into two main categories:
- Functional Testing: We check whether the behavior of the application is as per the pre-defined needs.
- Non-functional Testing: We check how the software works or performs under different conditions like stress, load, or across distinct environments.
Now, there are testing types within the above-mentioned categories:
Functional Testing Types
- White-box Testing: White-box testing pertains to testing based on knowledge of the internal structure, logic, and functionalities of the software being tested.
- Block-box Testing: In black box testing, the tester has no knowledge about the software system’s internal workings.
- Ad hoc Testing: Here, the testers either find or break bugs in an environment without following pre-determined documentation or tests.
- API Testing: API (Application Programming Interfaces) checks whether the interfaces between software components operate in a reliable and correct manner. API testing forms a crucial aspect of API management.
- Exploratory Testing: This helps software testers determine hard-to-predict situations or scenarios that can cause software errors.
- Regression Testing: In regression testing, we find out whether the new features can degrade or break the present functionality. It makes sure that new tests do not introduce new defects in the system.
- Sanity Testing: Sanity testing verifies whether particular functionalities work as intended. This testing is used to check the working of the menus as well as functions and commands when there is no time to go for regression testing.
- Smoke Testing: Smoke testing is a rudimentary testing process that checks whether the core functions of the software application work as per the expectation. This is done to check whether the prototype is stable enough for further testing.
- User Acceptance Testing: It is a specialized type of acceptance testing carried out by the end users to ascertain whether the system aligns with the users’ needs and functions as expected in real-world scenarios.
Non-functional Testing Types
- Recovery Testing: This testing checks how the software responds to failures and recovers from it. This verifies whether the processes and data can be restored correctly after the failure.
- Performance Testing: Performance testing involves checking how the software performs under distinct load conditions.
- Load Testing: It is a type of performance testing that checks performance under real-life load balancing conditions.
- Stress Testing: As the name suggests, it checks how much strain the system can tolerate before the failure occurs.
- Security Testing: This checks whether there are defects or faults that hackers or malicious sources can exploit.
- Usability Testing: Usability checks how effectively a customer can navigate the UI of the system to complete the tasks intuitively and efficiently.
- Compatibility Testing: In this testing, we check the functioning of the software across diverse devices, operating systems, network environments, and browsers.
Also Learn: Selenium Interview Questions: Top 30 Questions You Must Know
What Are the Different Challenges in Software Testing?

Despite its core advantages, software testing also introduces a few challenges of its own:
- Understanding Techniques and Technology: Accelerated technological expansion need testers to consistently learn and adjust, staying consistent with the latest tools and methodologies.
- Relationship and Communication Management: Effective collaboration between developers, testers, and stakeholders is quite complex because of possible gaps and misaligned expectations.
- Testing Proficiency: Recognizing complex bugs and handling test suites require specialized skills and a strategic approach to make sure that the testing is effective and thorough.
- Environment and Processes: Unstable environments of testing and unclear processes can impact accurate testing and protract the development process, enhancing the risk of defects.
Conclusion
Software testing has emerged as a vital component of advanced software development, impacting product quality directly while also influencing cost efficiency and security. Organizations that focus on complete testing methodologies, both automated and manual, position themselves to provide secure and reliable applications while reducing costly post-release failures. The Delta Air Lines incident is a great example that demonstrates the importance of testing in avoiding major system failures. As technology evolves consistently, development teams must adopt powerful software testing frameworks at every level in the software development lifecycle, making sure that the software aligns with the user expectations and technical specifications while ensuring competitive edge in an increasingly competitive IT industry.
Related Read: 5 Database Load Testing Strategies for High-Traffic Applications
Respond to this article with emojis