Microsoft Outlook users working with Exchange Server environments often encounter situations where accessing offline storage becomes problematic. Email data stored in OST format can become inaccessible due to server connectivity
Microsoft Outlook users working with Exchange Server environments often encounter situations where accessing offline storage becomes problematic. Email data stored in OST format can become inaccessible due to server connectivity issues, profile corruption, or system migration requirements. Market trends show growing demand for solutions that convert ost to pst, enabling users to recover mailbox data independently from Exchange infrastructure. Understanding the relationship between OST and PST formats provides essential knowledge for addressing these data accessibility challenges effectively.
What are OST and PST Files in Microsoft Outlook
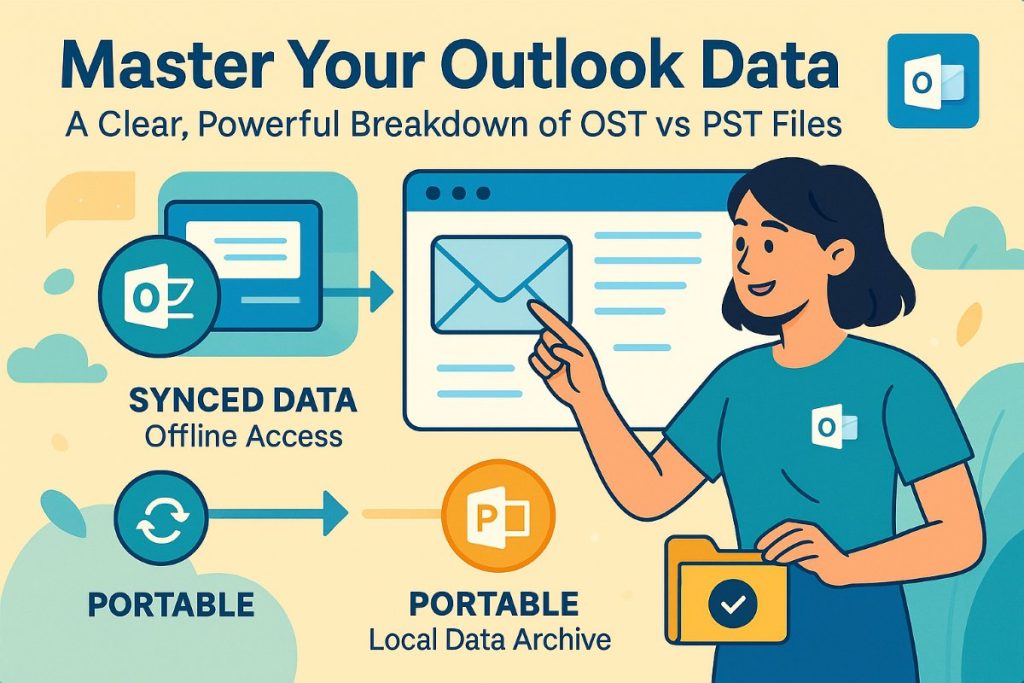
Microsoft Outlook employs two primary file formats for storing mailbox data on local systems. Each format serves specific purposes within different email account configurations and operational contexts.
OST File Characteristics and Functions
OST (Offline Storage Table) files are created automatically when Outlook connects to Exchange Server, Office 365, or IMAP accounts in Cached Exchange Mode. These files function as synchronized replicas of server-based mailboxes, enabling users to access email content without active network connections.
Key characteristics of OST files:
- Automatic synchronization with Exchange Server upon re-establishing connectivity
- Encryption via MAPIEntryID keys with GUIDs bound to user profiles
- Support for composing, deleting, and managing email folders offline
- Architecture dependent on the server; with a need to create an original profile for file access.
- Size limits depend on the Outlook version, with modern ones usually going up to 50GB.
Changes made offline are queued and synchronized with the Exchange Server when it is connected again, ensuring consistency of data across systems.
PST File Purpose and Applications
PST (Personal Storage Table) files serve as independent storage containers for Outlook data. Unlike OST files, PST formats operate without server synchronization requirements, making them portable across different systems and Outlook installations. PST archives are often used in many workplace setups when users precisely organize their email data with communication platforms such as Microsoft Teams. This helps them maintain accessibility, transparency, and accountability in communication track records.
PST files are created for POP3 email accounts or when users manually establish personal storage locations. These files store complete copies of emails, attachments, contacts, calendar entries, tasks, and notes on local drives. The primary distinction lies in operational independence. While OST files require Exchange Server connectivity, PST files function as self-contained data repositories, making them valuable for backup procedures and email migration projects.
Common Scenarios Where Converting a Data File Might Be Necessary
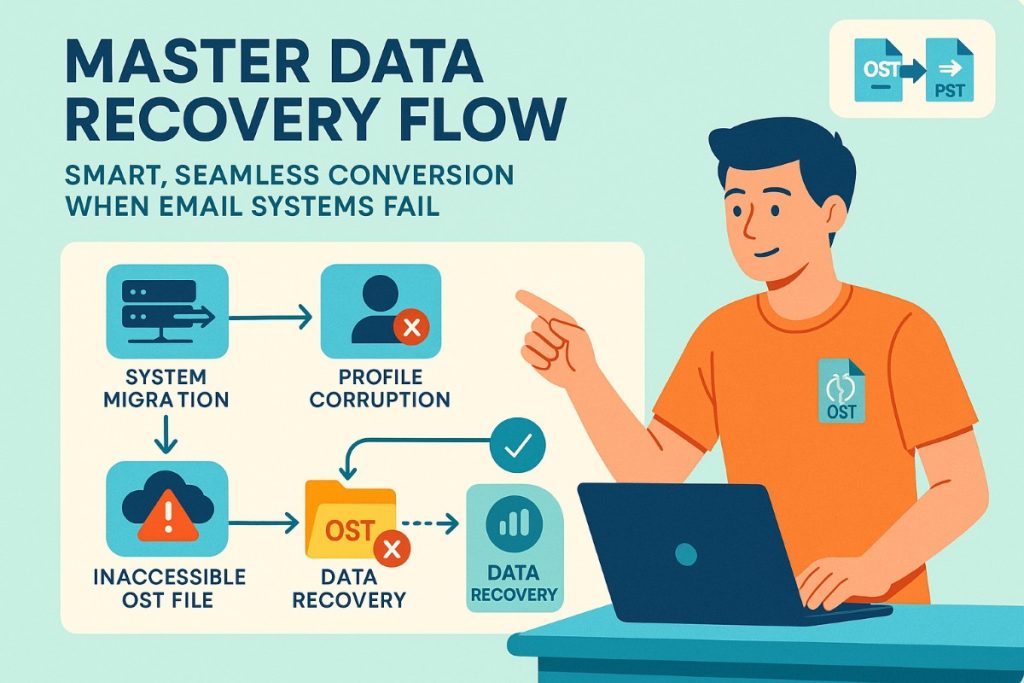
A number of technical and operational situations create valid requirements to convert offline storage files to personal storage format. Understanding these helps the organization prepare appropriate strategies for data management.
System Migration and Profile Issues
Email system migrations represent one of the most frequent conversion triggers. When organizations transition between email platforms, existing OST files cannot be directly imported into new environments. The files remain encrypted and bound to original Exchange profiles, preventing straightforward data transfer.
Profile corruption presents another common challenge. System failures, improper Outlook shutdowns, or registry errors can damage the MAPI profile linking users to their OST files, effectively creating orphaned files containing potentially critical business data.
Typical conversion scenarios include:
- Hardware replacement that involves transferring mailbox data to new systems
- Decommissioning of Exchange Servers with a need to preserve historical email records.
- Corruption of Outlook profile causing inability to access OST file as usual
- Recovery of oversized OST files exceeding the recommended size limits
- Migration to email clients that are incompatible with Exchange-specific file formats
Microsoft documentation identifies connection failures as primary causes of OST accessibility problems, particularly in environments with intermittent network connectivity.
Data Recovery After Server Disruptions
Exchange Server downtime renders users unable to synchronize their offline storage files. Though OST files contain a complete replica of the mailbox, this data is accessible either after the restoration of the server or by transforming the file into the independent PST format. Conversions brought about due to server issues commonly include hardware failure, malware attacks, or administrative errors during maintenance procedures.
Conversion Methods and Technical Approaches (OST to PST)

Multiple methods exist for transforming offline storage files into personal storage format, each with distinct advantages based on technical requirements and file conditions.
Manual Conversion Process
Microsoft Outlook supports the export of mailbox data using the native Import/Export wizard. This can be done manually when users have active Exchange Server connections.
Standard export procedure:
- Launch Microsoft Outlook with active Exchange profile configuration
- Go to the File menu and then click Open & Export options.
- Select Import/Export from the available menu choices
- Choose "Export to a file" in the Import and Export Wizard
- Specify Outlook Data File (.pst) as the export format
- Choose mailbox folders to export and set the inclusion of subfolders.
- Define destination path and filename for the resulting PST file
Manual conversion has some serious limitations. It needs Exchange Server connectivity, and thus it is not applicable in the case of orphaned OST files or if the access to servers is not available. It is incapable of handling multiple mailbox conversions in a single run and can't support damaged OST files once the integrity of the file is broken.
Alternative Conversion Solutions
Industry scrutiny has noted that customized conversion utilities overcome the inefficiencies of manual methods. Research from Gartner on email migration technologies indicate that organizations are increasingly using specialized utilities for complex data transfer scenarios, such as dealing with corrupted files and large-scale conversions.
Professional OST conversion utilities offer a number of technical advantages. There is no need for Exchange Server connections in order to process OST files, so such tools are suitable for orphaned file recovery. They can also handle batch processing to convert multiple OST files simultaneously. Advanced tools preserve complete folder hierarchies and maintain email metadata including timestamps and sender information.
Best Practices for Email Data Management
Implementation of structured approaches in file conversion minimizes data losses and ensures the success of the operation.
Pre-conversion preparation steps:
- Verify available disk space accommodates both source OST and resulting PST files
- Create backup copies of the original OST files in separate storage locations.
- Close all mail-enabled applications to avoid file access conflicts.
- Document current Outlook profile configurations and settings
- Test conversion procedures with non-critical mailboxes prior to processing important data.
Verification of post-conversion integrity takes place. Resulting PSTs should be imported into installations of Outlook by the user, going through folder structures systematically, validating calendar entries and contact information transferred correctly.
Key takeaways for successful conversion:
- Regular backups prevent data loss from file corruption or system failure.
- Understanding OST and PST differences helps select appropriate storage strategies.
- Professional conversion tools offer reliability when dealing with damaged or orphaned files.
- Testing data conversion processes on sample data minimizes risks within production environments.
Respond to this article with emojis